The way we interact with technology is evolving faster than ever before. After decades of working through screens and keyboards, we’re stepping into a new era—spatial computing. By blending the digital and physical worlds, spatial computing is enabling immersive experiences that are redefining how businesses operate, engage customers, and innovate.
From augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to mixed reality (MR) and AI-driven 3D environments, spatial computing is already reshaping industries such as retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and real estate. And this is just the beginning.
In this article, we’ll explore what spatial computing is, how immersive experiences are being applied in business today, and where this transformative technology is headed in the future.
What is Spatial Computing?
Spatial computing is the practice of interacting with digital information in three-dimensional (3D) spaces rather than on flat screens. It leverages technologies like:
- AR (Augmented Reality): Overlaying digital content on the real world.
- VR (Virtual Reality): Fully immersive digital environments.
- MR (Mixed Reality): Blending physical and digital worlds where both interact.
- AI + IoT + 5G: Making these immersive experiences intelligent and responsive in real-time.
Essentially, spatial computing lets us work, shop, collaborate, and play inside digital layers that coexist with our physical environment.
The Rise of Immersive Experiences in Business
Businesses are quickly realizing that immersion drives engagement, efficiency, and innovation. Unlike flat-screen experiences, immersive environments create stronger emotional connections and more intuitive ways of interacting with data, products, and people.
Here are key industries embracing spatial computing today:
1. Retail & E-commerce
- Now: Virtual try-ons (clothes, furniture, makeup) let customers preview products before buying.
- Example: IKEA’s AR app allows customers to see how furniture looks in their homes.
- Future: Fully immersive virtual stores where customers walk through digital aisles, interact with AI shopping assistants, and make purchases seamlessly.
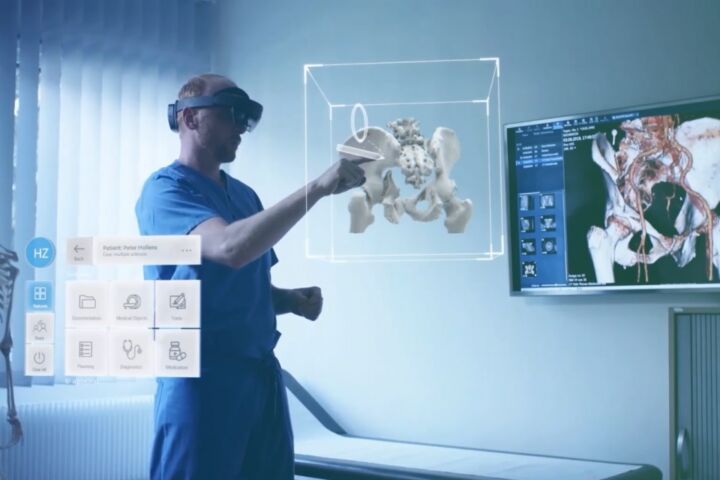
2. Healthcare & Medical Training
- Now: Surgeons use AR headsets for guided operations, while VR provides lifelike simulations for medical students.
- Example: Mayo Clinic uses VR to train surgeons in complex procedures.
- Future: Spatial computing will enable AI-driven virtual patients for risk-free practice and remote tele-surgery where specialists operate across continents.
3. Manufacturing & Industrial Training
- Now: Factories use VR simulations to train workers safely.
- Example: Boeing uses AR glasses to guide technicians in assembling complex wiring.
- Future: Entire digital twins of factories will let AI agents simulate and optimize operations before changes happen in the real world.
4. Real Estate & Architecture
- Now: Buyers explore properties through VR tours.
- Example: Matterport’s 3D scans allow remote property visits.
- Future: Architects and clients will co-create designs in real-time within mixed-reality environments, speeding up approvals and construction timelines.
5. Corporate Collaboration & Training
- Now: Businesses use VR spaces for remote meetings and immersive team-building.
- Example: Accenture built a virtual campus for employee onboarding.
- Future: Immersive collaboration will replace video calls, with teams meeting in persistent 3D workspaces where AI copilots assist in brainstorming and planning.
Benefits of Spatial Computing in Business
- Enhanced Customer Engagement – Immersive shopping increases satisfaction and reduces returns.
- Faster Learning & Training – VR/AR training reduces risks and improves retention.
- Increased Efficiency – Digital twins allow pre-testing of strategies and designs.
- Global Collaboration – Teams can work together in shared immersive spaces.
- New Revenue Streams – Virtual products, immersive advertising, and branded AR experiences.
Challenges in Adopting Spatial Computing
While the potential is massive, businesses face hurdles:
- Hardware Limitations – Headsets are still bulky and expensive.
- High Development Costs – Creating immersive content requires resources.
- Integration Issues – Blending with existing IT infrastructure can be complex.
- User Adoption – Not all employees or customers are ready for immersive tech.
- Privacy & Security – Collecting spatial data raises ethical concerns.
The Future of Spatial Computing in Business
Looking ahead, spatial computing will move from experimental to essential. Here are some future trends:
1. AI + Spatial Computing Fusion
AI agents will enhance immersive experiences by making environments context-aware, personalized, and autonomous.
2. Hyper-Personalized Retail
Every shopper will see a store tailored to their preferences, browsing histories, and real-world context.
3. Metaverse for Enterprises
Businesses will create persistent digital campuses for employees, partners, and customers.
4. Immersive Data Visualization
Executives will walk through 3D dashboards where data is spatially represented for faster insights.
5. Widespread AR Glasses Adoption
As AR glasses become mainstream (Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest, Microsoft HoloLens), immersive workspaces will replace laptops and smartphones for many tasks.
Final Thoughts
Spatial computing is more than a buzzword—it’s a paradigm shift in how humans and machines interact. Businesses today are already reaping benefits through immersive experiences in retail, healthcare, training, and real estate.
In the future, as AI, AR, VR, and IoT converge, we’ll see entire industries rebuilt around spatial-first business models. Immersive experiences will not just complement traditional methods—they’ll become the primary way we work, shop, learn, and collaborate.
The organizations that embrace spatial computing early will gain a competitive edge in creating richer customer experiences, smarter operations, and future-ready workplaces.

